Conformance
Statement for the
NINA DICOM Archive
Peter Müller
Christian Falk
Elimpex
Medizintechnik
Version 1.0.0
8 October 2002
A Introduction
The NINA DICOM Archive uses DICOM as the interface to
the external world. The server accepts DICOM association requests for the
purpose of storing images and for image query and retrieve. The NINA DICOM
Archive will initiate DICOM association requests for the purpose of sending
images to an external server. The NINA DICOM Archive does not respond to any
other type of network communication.
A.1 Implementation Model
The NINA DICOM Archive provides for storage and
query/retrieval of images. It runs on Unix systems as a background process that
accepts association requests from external applications. For each association
request, the NINA DICOM Archive forks a copy of itself so that the copy
communicates exclusively with the requesting application.
The NINA DICOM Archive will initiate a DICOM association
in response to a move request from an external application.
The NINA DICOM Arichive is started at system startup by the Unix rc command
startup system.
A.1.1 Application Data Flow Diagram
Figure 1 shows the relationship of the NINA DICOM
Archive application to external applications. As noted above, the NINA DICOM
Archive does not initiate any action except in response to requests which are
received via DICOM communication.
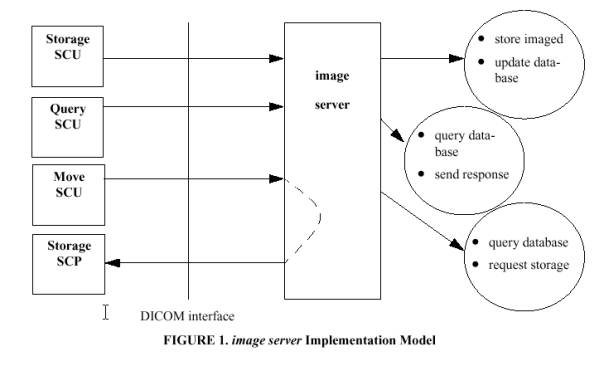
A.1.2 Functional Definition of Application Entities
The NINA DICOM Archive waits for another application
to connect at the TCP/IP port number specified when the application is
initiated. When another application makes a DICOM association request, the NINA
DICOM Archive uses a control database and logic to verify the request:
1. The NINA DICOM Archive uses a control table to
verify that the Called Application Title used in the associ-ation request is
defined on the node (Unix host-name) upon which the NINA DICOM Archive is
running.
2. The NINA DICOM Archive uses a control table to
lookup the application defined by the Calling Application Title in the
association request. The NINA DICOM Archive verifies that the node from which
the call origi-nated matches the value stored in the control table.
A.1.3 Sequencing of Real-World Activities
The NINA DICOM Archive has no way of knowing when it
has a complete study or what constitutes a complete study. If it receives an
image query while also receiving storage requests, the query response may not
include all of the images that are in the study.
A.2 AE Specifications
The NINA DICOM Archive may be invoked multiple times
on a single machine and the instances may operate simultaneously. In addition,
each time the NINA DICOM Archive receives an association request, it forks a
copy of itself. Each invocation and each forked copy of the NINA DICOM Archive
represent the same Application Entity.
A.2.1 AE NINA DICOM Archive – Specification
The NINA DICOM Archive provides Standard Conformance
to the following DICOM 3.0 SOP Classes as an SCU:
TABLE 1. SOP Classes Supported by NINA DICOM Archive
as an SCU
|
SOP Class Name |
SOP Class UID |
|
Computed Radiography Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1 |
|
CT Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 |
|
Ultrasound Multi-Frame Image
Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.3 |
|
MR Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.4 |
|
Nuclear Medicine Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.20 |
|
Ultrasound Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.6 |
|
Secondary Capture Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.7 |
|
X-Ray Angiographic Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1.12.1 |
|
X-Ray Radiofluoroscopic Image
Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1.12.2 |
The NINA DICOM Archive provides Standard Conformance
to the following DICOM 3.0 SOP Classes as an SCP:
TABLE 2. SOP Classes Supported by NINA DICOM Archive
as an SCP
|
SOP Class Name |
SOP Class UID |
|
Verification SOP Class |
1.2.840.10008.1.1 |
|
Computed Radiography Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1 |
|
CT Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 |
|
Ultrasound Multi-Frame Image
Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.3 |
|
MR Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.4 |
|
Nuclear Medicine Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.20 |
|
Ultrasound Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.6 |
|
Secondary Capture Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.7 |
|
X-Ray Angiographic Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1.12.1 |
|
X-Ray Radiofluoroscopic Image
Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1.12.2 |
|
|
|
|
Patient Root Query/Retrieve Info
Model - FIND |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2.1.1 |
|
Patient Root Query/Retrieve Info
Model - MOVE |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2.1.2 |
|
Study Root Query/Retrieve Info
Model - FIND |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2.2.1 |
|
Study Root Query/Retrieve Info
Model - MOVE |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2.2.2 |
A.2.1.1 Association Establishment Policies
A.2.1.1.1 General
The NINA DICOM Archive will attempt to initiate
associations in response to C-MOVE requests from other Application Entities.
The NINA DICOM Archive will only initiate associations in reponse to valid
C-MOVE requests for images that are known to the server (stored in its
database).
The maximum PDU size which can be transmitted by the
NINA DICOM Archive is fixed at 16KB. The default maximum PDU size which can be
received by the NINA DICOM Archive is configurable with a default value of 16KB
and a maximum value of 32KB.
A.2.1.1.2 Number of Associations
The number of simultaneous associations which will be
accepted by the NINA DICOM Archive are limited only by the kernel parameters of
the underlying TCP/IP implementation. The NINA DICOM Archive will spawn a new
process for each association request that it receives. Therefore, the NINA
DICOM Archive can have multiple simultaneous connections, and there is no
inherent limitation on the total number of simultaneous associations which the
NINA DICOM Archive can maintain. The NINA DICOM Archive does limit each
external Entity to no more than two simultaneous associations.
A.2.1.1.3 Asynchronous Nature
The NINA DICOM Archive does not support asynchronous
operations and will not perform asynchronous win-downegotiation.
A.2.1.1.4 Implementation Identifying Information
The NINA DICOM Archive will provide an implementation
class UID which is 1.2.826.01.368003.2.242.1.2 .
The NINA DICOM Archive will provide an implementation
version name of
Elimpex NINA 1.0
A.2.1.2 Association Initiation Policy
The NINA DICOM Archive attempts to initiate one
association in response to each C-MOVE command it receives from an external
node. The NINA DICOM Archive attempts a single type of association request.
A.2.1.2.1 Real-World Activity - Move Request from an
External Node
A.2.1.2.1.1 Associated Real-World Activity - Move Request
from an External Node
The associated Real-World activity is a C-MOVE request
from an external application. If an applica-tion successfully establishes an
association with the NINA DICOM Archive and makes a valid C-MOVE request that
identifies one or more images known by the NINA DICOM Archive, the NINA DICOM
Archive will intiate an associ-ation with the destination specified in the
C-MOVE request.
A.2.1.2.1.2 Proposed Presentation Contexts
In response to a C-MOVE request, the NINA DICOM
Archive builds a complete list of images to be moved. The list includes the SOP
class of each image to be moved. The NINA DICOM Archive extracts the unique SOP
classes from the image lists and proposes a set of presentation contexts that
includes one presentation context for each unique SOP class identified in the
image list. Thus, the association request may have a single presentation
context or multiple presentation contexts. Each presentation context contains
the abstract syntax that identifies one image class as found in the image list.
TABLE 3. Proposed Presentation Contexts for NINA DICOM
Archive
|
Presentation Context Table |
|||||
|
Abstract Syntax |
Transfer Syntax |
Role |
Extended Negotiation |
||
|
Name |
UID |
Name List |
UID List |
||
|
See note |
See note |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian Transfer Syntax |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCU |
None |
Note: The Abstract Syntax corresponds to the value
found in the database maintained by the each server. More than one presentation
context can be offered, each with a different abstract syntax.
Note: The NINA DICOM Archive only supports Implicit VR
Little Endian Transfer Syntax. Some images may have been stored by the NINA
DICOM Archive with private elements whose encoding scheme is unknown by the
NINA DICOM Archive. These elements will be transmitted by the NINA DICOM
Archive exactly as they were received (in Implicit VR Little Endian Transfer
Syntax), so they should be unaltered upon transmission.
A.2.1.2.2 SOP Specific Conformance Statement
All C-STORE operations are in the context of a C-MOVE
request from an external node.
The NINA DICOM Archive sends one C-MOVE response
message for each attempted C-STORE operation. The NINA DICOM Archive takes no
action in response to a failure or warning status.
The NINA DICOM Archive does not attempt any extended
negotiation.
The NINA DICOM Archive does not delete any elements
from the files it transfers. Therefore the set of optional elements depends
entirely on the contents of the files which were originally stored on the NINA
DICOM Archive.
In the event that the NINA DICOM Archive receives an
unsuccessful C-STORE response, the NINA DICOM Archive will continue sending the
remaining images in the requested set.
A.2.1.3 Association Acceptance Policy
The NINA DICOM Archive accepts associations for the
purpose of storing images in its database or for the pur-pose of performing
query/retrieve operations on the images that have been previously stored.
The NINA DICOM Archive will only accept association
requests from applications that are defined during con-figuration.In addition, the
NINA DICOM Archive will only store images sent by nodes that have been enabled
by a configuration step.
A.2.1.3.1 Real-Word Activity - Storage
The NINA DICOM Archive accepts associations from nodes
that wish to store images using the C-STORE com-mand.
A.2.1.3.1.1 Associated Real-World Activity
The associated Real-World activity associated with the
C-STORE operation is the storage of theimage on the disk of the system upon
which the NINA DICOM Archive is running. Images are stored by writing the data
set of the C-STORE command directly to disk with no further header or
interpretation. After the image is stored to disk, the NINA DICOM Archive
updates an image database with patient, study, series and image information;
this image database can be used by the NINA DICOM Archive for query/retrieve
operations.
The NINA DICOM Archive will issue a failure status if
it is unable to store the image on disk, if the image does not conform to the
IOD of the SOP class under which it was transmitted, or if the NINA DICOM
Archive is not able to successfully update its image database.
A.2.1.3.1.2 Presentation Context Table
Any of the Presentation Contexts shown in Table 4 are
acceptable to the NINA DICOM Archive for receiving images
TABLE 4. Acceptable Presentation Contexts for the NINA
DICOM Archive
|
Presentation Context Table |
|||||
|
Abstract Syntax |
Transfer Syntax |
Role |
Extended Negotiation |
||
|
Name |
UID |
Name |
UID |
||
|
Computed Radiograhy Image |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
CT Image |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 |
‘’ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Ultrasound Multi-Frame Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.3 |
‘’ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
MR Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.4 |
‘’ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Nuclear Medicine Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 0 |
‘’ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Ultrasound Image |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.6 |
‘’ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Secondary Capture Image |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.7 |
‘’ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
X-Ray Angiographic Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.1.12. 1 |
“ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
X-Ray Radiofluoro- scopic Image Storage |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.1.12. 2 |
“ |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
A.2.1.3.1.2.1 SOP Specific Conformance for SOP Class
Storage
The NINA DICOM Archive implements Level 2 (Full)
conformance for the Storage SOP Class.
The following attributes are modified by converting
all characters to upper case before data is stored in the image database. The
image files themselves are not modified.
1. Patient Name
2. Patient ID
3. Accession Number
4. Study ID
In the event that an image is successfully stored by
the NINA DICOM Archive, it may be accessed by requesting associations with the
NINA DICOM Archive and performing query/retrieve operations. The NINA DICOM
Archive is not designed to allow other access to stored images.
The NINA DICOM Archive stores images for an indefinite
period. The system has no method for deleting images once they are stored.
The NINA DICOM Archive returns the following status
values in response to a C-STORE request:
0000H Image successfully stored
A700H Refused - out of resources (unable to create
local file)
A900H Error- data set does not match SOP Class
C000H Error - cannot understand
A.2.1.3.1.3 Presentation Context Acceptance Criterion
The NINA DICOM Archive will accept any number of
storage SOP classes that are listed in Table 4 above, pro-vided that the
requesting application is known to the NINA DICOM Archive and has been enabled
to store images on the NINA DICOM Archive (via a configuration step). The NINA
DICOM Archive defines no limit on the num-ber of presentation contexts
accepted. In the event that the NINA DICOM Archive runs out of resources when
trying to accept ultiple presentation contexts, the NINA DICOM Archive will
reject the association request.
The NINA DICOM Archive does not check for duplicate
presentation contexts and will accept duplicate presen-tation contexts.
A.2.1.3.1.4 Transfer Syntax Selection Policies
The NINA DICOM Archive only supports the Implicit VR
Little Endian transfer syntax. Any proposed presenta-tion context which
includes the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax will be accepted with
the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax. Any proposed presentation
context that does not include the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax
will be rejected.
A.2.1.3.2 Real World Activity - Query
The NINA DICOM Archive accepts associations from nodes
that wish to perform query (find) and retrieve (move) operations on images that
have been previously stored by the NINA DICOM Archive.
A.2.1.3.2.1 Associated Real World Activity - Query
The real-world activity associated with C-FIND and
C-MOVE requests are the query and retrieval operations initiated by another
application. An application other than the NINA DICOM Archive queries the NINA
DICOM Archive for patient/study/series/image information that has been
previously stored by the NINA DICOM Archive and can request that the NINA DICOM
Archive send images to a third application.
A.2.1.3.2.2 Presentation Context Table
Table 5 shows the presentation contexts that may be
accepted by the NINA DICOM Archive for query opera-tions.
TABLE 5. Acceptable Presentation Contexts for Query
Classes
|
Presentation Context Table |
|||||
|
Abstract Syntax |
Transfer Syntax |
Role |
Extended Negotiation |
||
|
Name |
UID |
Name |
UID |
||
|
Patient Root Query/ Retrieve Information Model - FIND |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 .1.1 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Patient Root Query/ Retrieve Information Model - MOVE |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 .1.2 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Study Root Query/ Retrieve Information Model - FIND |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 .2.1 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Study Root Query/ Retrieve Information Model - MOVE |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 .2.2 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Patient StudyOnly Query/Retrieve Informa-tion Model - FIND |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 .3.1 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
|
Query/Retrieve Informa-tion Model - MOVE |
1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.2 .3.3 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
A.2.1.3.2.2.1 SOP Specific Conformance for SOP Class
Query/Retrieve
The NINA DICOM Archive does not support relational
searches. Table 6 below indicates which keys are sup-ported by the NINA DICOM
Archive for the patient root information model. The NINA DICOM Archive also
supports the patient/study only information model. The keys supported for that
model are the same keys found in Table 6 with a level of “Patient” or “Study”.
Table 8 indicates which keys are supported by the NINA DICOM Archive for the
study root information model. These tables include the optional and required
keys that are supported. Optional keys are supported like required keys. The
NINA DICOM Archive does not support relational queries.
TABLE 6. Keys Supported for Patient Root Information
Mode
|
Level |
Description |
Tag |
Type |
|
Patient |
Patient Name |
0010 0010 |
R |
|
Patient |
Patient ID |
0010 0020 |
U |
|
Patient |
Patient Birth Date |
0010 0030 |
O |
|
Patient |
Patient Birth Time |
0010 0032 |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patient |
Patient Sex |
0010 0040 |
O |
|
Study |
Study Date |
0008 0020 |
R |
|
Study |
Study Time |
0008 0030 |
R |
|
Study |
Accession Number |
0008 0050 |
R |
|
Study |
Study ID |
0020 0010 |
R |
|
Study |
Study Instance UID |
0020 000D |
U |
|
Study |
Referring Physican Name |
0008 0090 |
O |
|
Study |
Study Description |
0008 1030 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient’s Age |
0010 1010 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient’s Size |
0010 1020 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient’s Weight |
0010 1030 |
O |
|
Series |
Modality |
0008 0060 |
R |
|
Series |
Series Number |
0020 0011 |
R |
|
Series |
Series Instance UID |
0020 000E |
U |
|
Series |
Body Part Examined |
0018 0015 |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Image |
Image Number |
0020 0013 |
R |
|
Image |
SOP Instance UID |
0008 0018 |
U |
|
Image |
SOP Class UID |
0008 0016 |
O |
|
Image |
Samples Per Pixel |
0028 0002 |
O |
|
Image |
Rows |
0028 0010 |
O |
|
Image |
Columns |
0028 0011 |
O |
|
Image |
Bits Allocated |
0028 0100 |
O |
|
Image |
Bits Stored |
0028 0101 |
O |
|
Image |
Pixel Representation |
0028 0103 |
O |
The NINA DICOM Archive supports the three MOVE SOP
classes listed in Table 5. In response to a move request, the NINA DICOM
Archive supports the Storage SOP classes that are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 7. Keys Supported for Study Root Information
Model
|
Level |
Description |
Tag |
Type |
|
Study |
Study Date |
0008 0020 |
R |
|
Study |
Study Time |
0008 0030 |
R |
|
Study |
Accession Number |
0008 0050 |
R |
|
Study |
Patient Name |
0010 0010 |
R |
|
Study |
Patient ID |
0010 0020 |
R |
|
Study |
Study ID |
0020 0010 |
R |
|
Study |
Study Instance UID |
0020 000D |
U |
|
Study |
Referring Physican Name |
0008 0090 |
O |
|
Study |
Study Description |
0008 1030 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient Birth Date |
0010 0030 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient Birth Time |
0010 0032 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient Sex |
0010 0040 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient’s Age |
0010 1010 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient’s Size |
0010 1020 |
O |
|
Study |
Patient’s Weight |
0010 1030 |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series |
Modality |
0008 0060 |
R |
|
Series |
Series Number |
0020 0011 |
R |
|
Series |
Series Instance UID |
0020 000E |
U |
|
Series |
Body Part Examined |
0018 0015 |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Image |
Image Number |
0020 0013 |
R |
|
Image |
SOP Instance UID |
0008 0018 |
U |
|
Image |
SOP Class UID |
0008 0016 |
O |
|
Image |
Samples Per Pixel |
0028 0002 |
O |
|
Image |
Rows |
0028 0010 |
O |
|
Image |
Columns |
0028 0011 |
O |
|
Image |
Bits Allocated |
0028 0100 |
O |
|
Image |
Bits Stored |
0028 0101 |
O |
|
Image |
Pixel Representation |
0028 0103 |
O |
A.2.1.3.2.3 Presentation Context Acceptance Criteria
The NINA DICOM Archive will accept any number of query
SOP classes that are listed in Table 5 above, pro-vided that the requesting
application is known to the NINA DICOM Archive and has been enabled to make
requests from the NINA DICOM Archive (via a configuration step). The NINA DICOM
Archive defines no limit on the number of presentation contexts accepted. In
the event that the NINA DICOM Archive runs out of resources when trying to
accept multiple presentation contexts, the NINA DICOM Archive will reject the
association
request.
The NINA DICOM Archive does not check for duplicate
presentation contexts and will accept duplicate presen-tation contexts.
A.2.1.3.2.4 Transfer Syntax Selection Policies
The NINA DICOM Archive only supports the Implicit VR
Little Endian transfer syntax. Any proposed presenta-tion context which
includes the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax will be accepted with
the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax. Any proposed presentation
context that does not include the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax
will be rejected.
A.2.1.3.3 Real World Activity - Verification
The NINA DICOM Archive accepts associations from nodes
that wish to perform a verification operation on the NINA DICOM Archive.
A.2.1.3.3.1 Associated Real World Activity -
Verification
The real-world activity associated with the C-ECHO
request is that an external node wishes to verify network or server operation
without initiating any actual work.
A.2.1.3.3.2 Presentation Context Table
Table 8 shows the presentation contexts that may be
accepted by the NINA DICOM Archive for verification operations.
TABLE 8. Acceptable Presentation Contexts for the NINA
DICOM Archive for Verification
|
Presentation Context Table |
|||||
|
Abstract Syntax |
Transfer Syntax |
Role |
Extended Negotiation |
||
|
Name |
UID |
Name |
UID |
||
|
Verification |
1.2.840.10008.1.1 |
DICOM Implicit VR Little Endian |
1.2.840.10008.1.2 |
SCP |
None |
A.2.1.3.3.2.1 SOP Specific Conformance for SOP Class
Verification
A.2.1.3.3.3 Presentation Context Acceptance Criterion
The NINA DICOM Archive will accept any number of
verification SOP classes that are listed in Table 8 above, provided that the
requesting application is known to the NINA DICOM Archive (via a configuration
step). The NINA DICOM Archive defines no limit on the number of presentation
contexts accepted. In the event that the NINA DICOM Archive runs out of
resources when trying to accept multiple presentation contexts, the NINA DICOM
Archive will reject the association request.
The NINA DICOM Archive does not check for duplicate
presentation contexts and will accept duplicate presen-tation contexts.
A.2.1.3.3.4 Transfer Syntax Selection Policies
The NINA DICOM Archive only supports the Implicit VR
Little Endian transfer syntax. Any proposed presenta-tion context which
includes the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax will be accepted with
the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax. Any proposed presentation
context that does not include the Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax
will be rejected.
A.3 Communication Profiles
A.3.1 TCP/IP Stack
The NINA DICOM Archive provides DICOM V3.0 TCP/IP
Network Communication Support as defined in Part 8 of the DICOM Standard.
A.3.1.1 TCP/IP API
The NINA DICOM Archive uses the TCP/IP stack from the
Unix system upon which it executes. It uses a sub-routine library that is based
on a Berkeley socket interface.
A.3.1.2 Physical Media Support
The NINA DICOM Archive exists as a software
application that can be compiled on various Unix platforms. As such, it places
no restrictions on the physical network. The NINA DICOM Archive has been
demonstrated using TCP/IP over Ethernet (Thick Wire, Thin Wire, 10 Base T),
FDDI (twisted pair into a concentrator, fiber backbone) and
Tin-Can-Telephone-Net.
A.4 Extensions/Specializations/Privatizations
Not applicable
A.5 Configuration
The NINA DICOM Archive obtains configuration
information from a “Control” database which is stored in a relational database.
In this implementation, the relational database is POSTGRES.
A.5.1 AE Title/Presentation Address Mapping
The control table “ApplicationEntity” is used to map
between AE Titles and Presentation Addresses.
A.5.2 Security Features
The NINA DICOM Archive uses three additional control
tables to control access. These tables allow the NINA DICOM Archive to
determine which nodes are allowed read and or write access and where images
should be stored.
A.5.3 Configurable Parameters
The following parameters may be configured for the
NINA DICOM Archive:
• Application
Entity Title
• TCP/IP Port
Number
A.5.4 Support of Extended Character Sets
The NINA DICOM Archive provides no
support for extended character sets.